Describing an Algorithm
Objectives
- Understand the logical steps involved in solving a problem using algorithms
- Know the difference between Structured English and Pseudocode
- Know how to express an algorithms using pseudocode
- Be able to read and comprehend algorithms represented in the form of flowcharts
- Understand that a computer program is an implementation of an algorithm; an algorithm is not a computer program
In the previous section we were working on an algorithm to find the largest value in a list of numbers: [23, 8, -76, 49, 65, -2]. We set out the steps using Structured English:
- Start with the first number in the list and consider it as the current maximum.
- Iterate through the remaining numbers in the list.
- For each number, compare it with the current maximum.
- If the current number is greater than the current maximum, update the current maximum to be that number.
- Continue this process until all numbers in the list have been considered.
- The final value of the current maximum is the maximum number in the list.
Structured English is a high-level description language that uses natural language constructs to represent the logic of a process or algorithm.
It is some step removed from the code used for a programming language. It is intended for humans to read who may not be familiar with the syntax or forms used in a formal programming language such as Python.
For GCSE Computer Science we need to be familiar with a more stylised form known as pseudocode and how flowcharts can also be used to describe an algorithm. Both AQA and OCR have their own versions of pseudocode and require students to express their answers to any questions requiring an algorithm using their version of pseudocode.
Note
For questions that require pseudocode answers, marks will still be awarded if the pseudocode is incorrect but the meaning of the algorithm remains sufficiently clear.
Pseudocode
Pseudocode is similar to Structured English in that they both provide high-level, human-readable representations of algorithms or processes without specifying the exact syntax of a particular programming language. However, there are some distinctions between the two:
| Structured English | Pseudocode |
|---|---|
| It often resembles a more natural language, using sentences and phrases to describe the steps of the algorithm in a way that is closer to everyday language. | It tends to have a structure that is more similar to code, using keywords and simple statements that are a bit closer to actual programming syntax |
| It is generally less formal and more human-readable. It is often used in the early stages of designing algorithms, providing a conceptual understanding of the process. | It can be a bit more formal and may include constructs that resemble programming language syntax. Pseudocode is often used as a transitional step between algorithm design and actual code implementation. |
| It is often intended for a broader audience, including stakeholders and individuals who may not have programming expertise. | It is typically geared more towards programmers or those with some familiarity with programming concepts. |
The finding the max algorithm becomes:
The pseudocode used above follows the form used by AQA.
The OCR version would be:
In both cases note how the pseudocode differs from the Structured English version. It look more like programming code but stops short of being an actual programming language. As programmers we can recognise assignment, a loop and a section statement, it may not take someone not familiar with programming that long to work out the purpose of this algorithm.
The pseudocode should express unambiguously the steps required to solve the given problem. We should be able to take the pseudocode and convert into the programming language of our choice: Python, C# etc..
Flowcharts
Another form we can use is a visual form, a diagram to represent the steps known as a flowchart.
The flowchart uses various shapes and arrows to illustrate the steps and the flow of control within that process. It is a diagrammatic tool that provides a clear and systematic way to represent the logical sequence of actions or decisions in a system.
They serve the same purpose as pseudocode and can be easier for non-programmers to follow and understand.
The flowchart uses a number of symbols to represent the steps in an algorithm and their sequence:
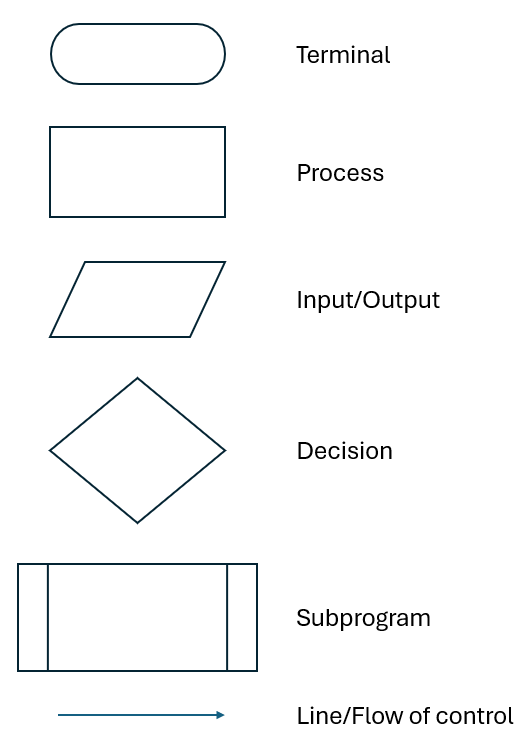
The flowchart for the find the maximum algorithm might be:
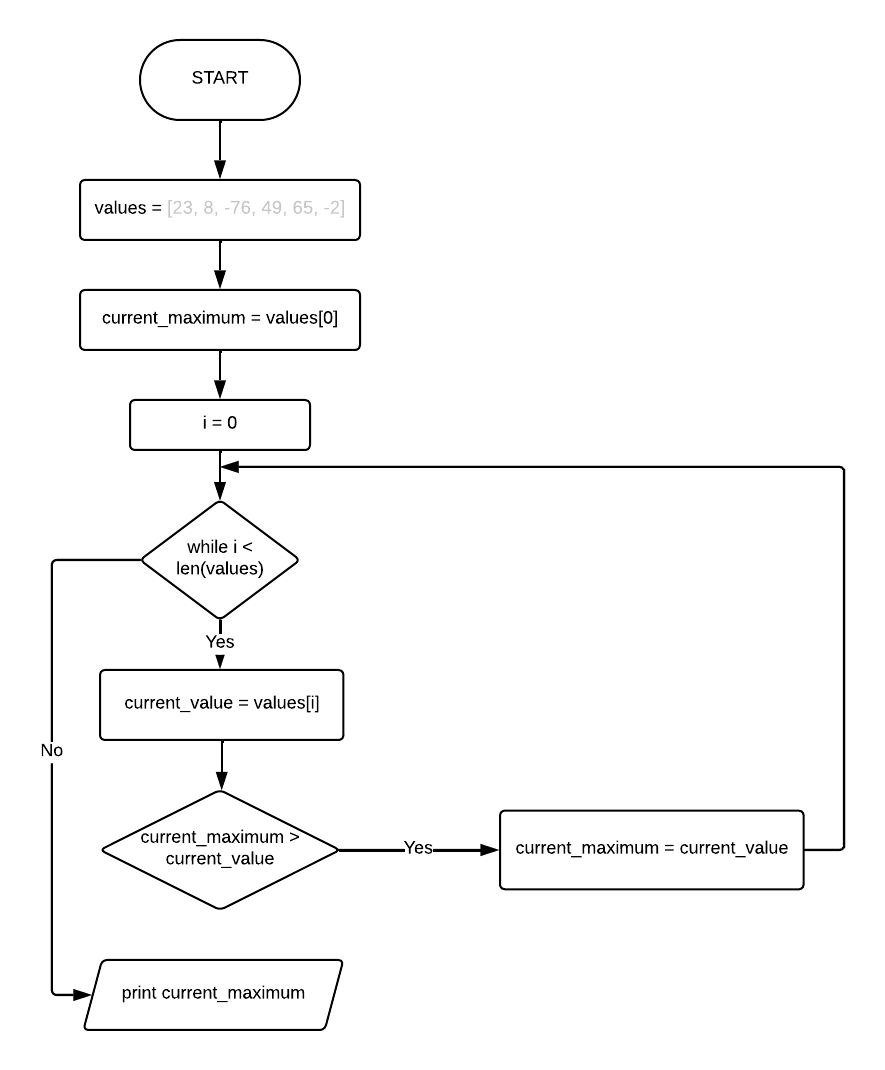
Flowcharts are a valuable tool for many situations. It is required for the GCSE that you both know how to create a flowchart and to read the algorithm from the given flowchart. However, they can be time consuming to construct and for more complex algorithms the diagrams quickly become large and fiddly to deal with. They do not handle detailed code well but are OK for high level view of an algorithm and useful for sketching ideas.