Selection, Boolean and Random
This content should also be familiar from the programming with Python topic but we need to see how this concept is described using pseudocode.
Selection
Recall that each line of code in a program will be executed one after the other in sequence unless we change the flow of control by introducing a construct such as selection or iteration.
With a selection statement the next statement to be executed will be dependent on some condition:
The condition, age > 17 is a boolean expression. It will evaluate to either True or False. In this example, age = 15, so the program will execute the print() statement that belongs to the else part of the selection block.
The if statement can provide a number of alternative branches:
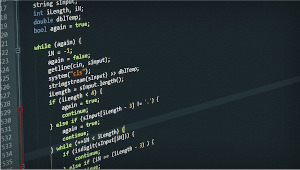
AQA pseudocode
Similar to previous example, do not forget the ENDIF:
OCR Pseudocode
Similar to previous example, except uses elseif instead of endif. Again, do not forget the endif:
Nested if statements
Another if statement can appear inside another one:
Switch/Case statement
Multiple if ... elif ... elif .. endif``` statements can sometimes be hard to follow and theswitch ... case`` statement block can make this easier to read and maintain:
Depending on the value entered by the user, the code will either take the first, second or third option. If none of these is recognised, it will default to the final alternative.
Note
AQA does not use switch/case in its pseudocode
Boolean Expressions
A number of operators are available for boolean expressions:
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
== |
Equal to | 7 == 7 |
True |
!= |
Not Equal to | 7 != 6 |
True |
> |
Greater than | 7 > 6 |
True |
< |
Less than | 7 < 6 |
False |
>= |
Greater than or equal to | 7 >= 7 |
True |
<= |
Less than or equal to | 7 <= 7 |
True |
Warning
Pay attention to the "is equal to" operator ( == ), it's two equal signs. It’s easy to mistake it for the assignment operator ( = ). It helps to read the assignment operator as e.g. "age is assigned the value 17" for age = 17; and "is age equal to 17?" for age == 17.
These are also known as the comparison operators
Complex Boolean Expressions
Boolean expressions can be joined together using AND, OR and NOT.
Random Number generation
Python has a built in library of functions for dealing with random numbers, and by using import random at the top of the program code makes the library available for use.
In the pseudocode, there is not need to add an import statement, it is assumed to be available.
AQA Pseudocode
OCR Pseudocode
Random number generation is not included in the OCR pseudocode